modules
Command Line 4
Unix
Unix (/ˈjuː.nɪks/; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, developed starting in the 1970s at the Bell Labs research center - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unix
Many Unix-like operating systems have arisen over the years, of which Linux is the most popular, having displaced SUS-certified Unix on many server platforms since its inception in the early 1990s. - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unix
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unix
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unix_philosophy
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_Unix
- http://www.howtogeek.com/182649/htg-explains-what-is-unix/
Why learn about this?
The rise of Linux mirrors the rise of the web, which just happens to have started around the same time. It’s hard to pin down exactly how popular Linux is on the web, but according to a study by W3Techs, Unix and Unix-like operating systems power about 67 percent of all web servers. At least half of those run Linux—and probably the vast majority. -https://www.wired.com/2016/08/linux-took-web-now-taking-world/
1) Most programmers will be using unix-based systems 2) Many of the same principles apply to all/or the vast majority of software systems you’re likely to encounter
Operating System Concepts
- Files and Processes
- “Everything is a file” (oversimplification, but a useful one)
- How does the operating system work?
ps auxto see the processes that are running, same as opening the “activity monitor”
- Exploring the root directory (in case you’re ever wondering what all those files in
/are)
Why?
Q: Isn’t this more than I need to know about computers?
A: Probably, but I want to show you that NOTHING is magic. If you ask “why” to anything, you should be able to get a straightforward answer. Learning to ask why and how can be an important management skill when it comes to tech projects in government.
Environment Variables and PATH
Evnironment Variables
Setting Environment Variables
export MY_VAR=1
Reading Environment Variables
echo $MY_VAR
Note how the environment variable is no longer defined once you exit out of the shell and reopen it. The ~/.bash_profile file is run every time you open a shell. You can store variables that you would like to persist in there.
Check out all of your environment variables: printenv
- some basic ones http://www.ee.surrey.ac.uk/Teaching/Unix/unix8.html
$PATH
$PATH is an environment variable that specifies where the executable programs are located.
which echofor example, will tell you where the echo command is located, it will be within one of the folders specified in$PATHotherwise you would have to call it explicitly every time as/bin/echo
❇️ Example: permanently setting an environment variable
Lets modify an environment variable inside your ~/.bash_profile (macOS) or ~/.bashrc (Ubuntu).
-
First
touch ~/.bash_profile(macOS) ortouch ~/.bashrc(Ubuntu) in the terminal. This will create an empty file in your home folder if one doesn’t already exist. If the file does exist, the touch command won’t modify it’s contents. -
Then open your
~/.bash_profile(macOS) or~/.bashrc(Ubuntu) file and place the following snippet at the bottom. This exports the environment variable PS1 which controls how your terminal display looks. All of the code inside this file is run every time you open a terminal.# set EDITOR as sublime text export EDITOR="subl --wait" # Define a function that returns your current git branch parse_git_branch() { git branch 2> /dev/null | sed -e '/^[^*]/d' -e 's/* \(.*\)/ (\1)/' } # Display present working directory and git path in bash prompt with colors export PS1="\u \[\033[32m\]\w\[\033[33m\]\$(parse_git_branch)\[\033[00m\] $ " -
Close and reopen the terminal to see the change. Modifying the PS1 environment variable as you just did creates this nice prompt that tells you where you are as you move around directories:

-
Modify PS1 within the existing shell (instead of in the bashrc/bash_profile). Notice that since we didn’t add this to the bashrc/bash_profile it doesn’t persist when we open a new tab.
Stdin & Stdout (& Stderr)
Originally I/O happened via a physically connected system console (input via keyboard, output via monitor), but standard streams abstract this. When a command is executed via an interactive shell, the streams are typically connected to the text terminal on which the shell is running, but can be changed with redirection, e.g. via a pipeline. - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Standard_streams
source: http://www.informit.com/articles/article.aspx?p=2273593&seqNum=5
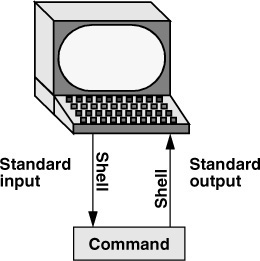
Figure 5-3 By default, standard input comes from the keyboard, and standard output goes to the screen
source: http://www.informit.com/articles/article.aspx?p=2273593&seqNum=5
Redirection
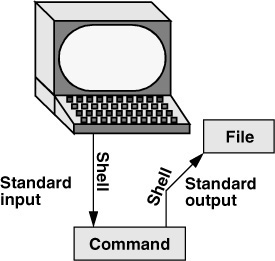
Figure 5-4 Redirecting standard output
command [arguments] > filename
source: http://www.informit.com/articles/article.aspx?p=2273593&seqNum=5
Piping

source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pipeline_(Unix)
and Exit Codes
Commands return exit codes when they finish running, 0is success, 1 is fail
Get exit code of the command you just ran with the following
echo $?
Error Codes other than 1 and 0 are more rare, but here are some examples.
Additional resource on exit codes:
https://shapeshed.com/unix-exit-codes/
Permissions and chmod
Observing a file’s permissions
The -l flag of the ls command lists information about files in the current directory in a long format. Among the details in the long format are file permissions.
ls -l


source: https://linuxcommand.org/lc3_lts0090.php
Check your knowledge
- Look at permissions inside
~/Development/universe/solar_system/planets - Look at permissions inside
/Applications- notice how those are executable while the planets files are not.
Changing a file’s permissions
chmod stands for “change mode”, it is the command that lets you set permissions for a file
- http://computerplumber.com/2009/01/using-the-chmod-command-effectively/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chmod
- https://www.cise.ufl.edu/~shray/
sudo (super user do)
Prepend any command with sudo in order to run the command as root user. Try to avoid this unless you know what you’re doing. But also know that it is often the solution if you get an error telling you that you don’t have the permissions to run something.
http://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/3063/how-do-i-run-a-command-as-the-system-administrator-root
❇️ Example
-
Make a file called
sayhello.pyin yourassignmentsfolder within~/Development.cd ~/Development/assignments touch sayhello.py -
Open
sayhello.pyand type the following python program:#!/usr/bin/env python3 import sys name = sys.stdin.read() print("Hello " + name + "!") -
Make sayhello.py executable.
chmod +x sayhello.py -
Run this program.
echo -n "John" | ./sayhello.py
➡️ Try It
This program below will add 1 to the input on STDIN.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import sys
input_number = sys.stdin.read()
print(int(input_number) + 1)
Save this program as a file called add1.py, chmod it, and execute it.